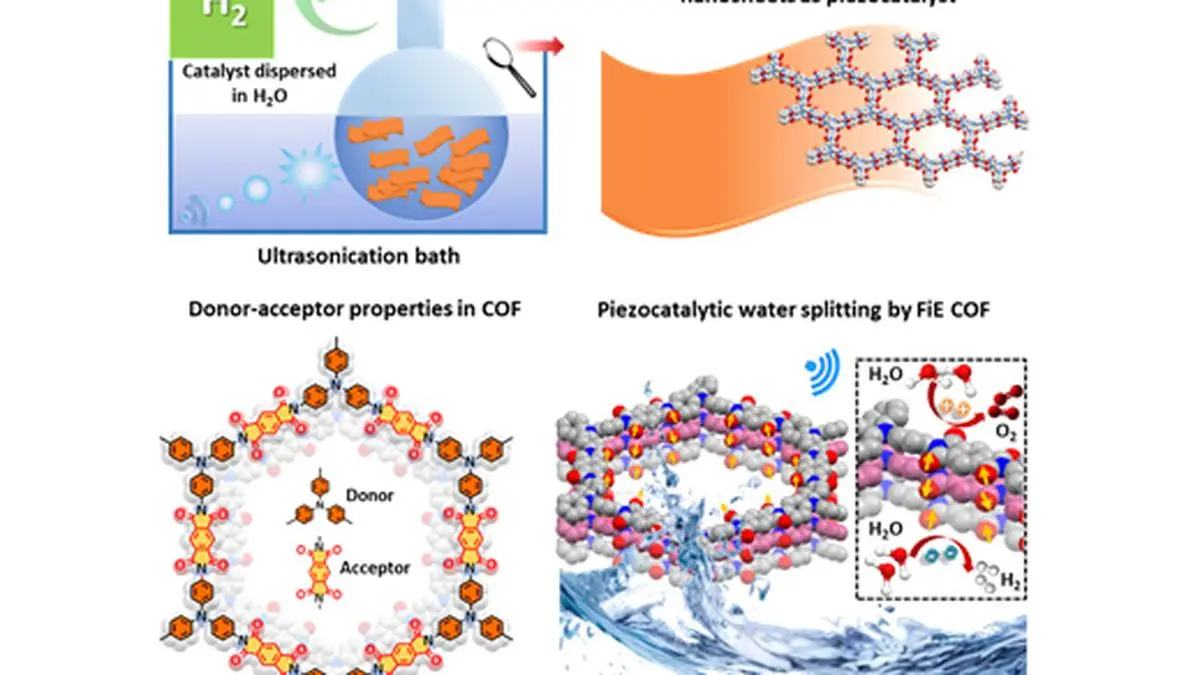
Piezocatalysis has become a promising catalytic technology that collects mechanical disturbances with a piezoelectric material to generate load carriers, which are used for catalysis of the water division. This is an environmentally benign method of hydrogen production and, in general, the water division stands out as an efficient and scalable technique that depends on catalysis.
In a recent innovative work, a team of researchers, led by Professor Tapas K Maji of the Materials Chemistry and Physics Unit at the Jawaharlal Nehru Center for advanced scientific research, Bengaluru, has developed a donor acceptor without covalent for) the division of piezocatalitic water of the forest. This study, published in advanced functional materials, demonstrates a COF construction from IMIDA links between the organic donor molecule Tris (4-aminophenyl) amine (cover) and the acceptor molecule of the pyromelitic molecule of the diandidrido diehydruro (fie), excitement, hunt Pastelite for water separation to produce hydrogen.
This discovery breaks the traditional notion of using only hardware (FE) based on heavy metal or transition as piezocatalizers for water division. Conventional faith materials have limited charges confined on the surface, which usually leads to a rapid saturation of their piezocatalitic activity. On the contrary, the request of FI in a COF provides a multipurpose number of loads on the pores surfaces, due to the large local electric fields. The sponge -shaped porous structure of a COF allows the dissemination of water molecules to access and use thesis affection for catalysis, which provides ultra high hydrogen production yields and exceed all inorganic piezocatalizers based on oxides.
Cheaper cholesterol test tool
Excessive cholesterol accumulation in the walls of the blood flow of blood flow | Photo credit: Rasi Bhadramani
A point of attention device (POC) has been developed to detect cholesterol in amounts of traces, even below the preferred range. It can be an efficient tool for routine monitoring or cholesterol levels.
It is a highly sensitive, ecological and profitable optical detection platform that can help identify early symptoms of diseases such as atherosclerosis, venous thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction.
The detection of fatal diseases in their first symptoms is essential, since abnormal biochemical markers can sometimes accompany such disorders. Therefore, the reliable detection of Biomarkers associated with thesis diseases is necessary for personalized health monitoring.
Cholesterol is an essential lipid in humans, produced by the liver. It is the precursor of vitamin D, bile acids and steroid hormones. Cholesterol is necessary for animal tissues, blood and nerve cells, and is transported by blood into mammals. There are two types of cholesterol: LDL (low density lipoprotein), or referring to ‘bad’ cholesterol because it can accumulate in the walls of the arteries and contribute to serious diseases, and the lipoprotein of the Cenanization HDL))
However, maintaining a balance in cholesterol levels is crucial. High and low cholesterol levels can lead to the disease. Atherosclerotic plates are formed when excess cholesterol accumulates in the walls of the artery, clean and annoying blood flow.
A team of interdisciplinary researchers from the Institute of Advanced Science and Technology Studies, Guwahati, has developed the optical detection platform for the detection of cholesterol based on silk fiber, which is functionalized using quantum phosphoren points.
More like this
Posted on May 18, 2025